Ethanol Plant Dynamic Model helps overcome design issues leading to smoother startup for a South Asia client. The downstream section of an Ethanol plant purifies the coming from the fermenter into valuable Ethanol. This section typically consists of a series of distillation columns and an evaporation section. Although, distillation being an open- form, many proprietary schemes are being offered by various designers. An engineering and turnkey supplier of Ethanol Plants, who have designed and commissioned many such plants, commissioned Equinox to build a steady-state & dynamic model of their new design, with the objective of studying the impact of design changes on the plant operability and fine-tuning of startup procedures, ultimately using the system to train plant operators in running the plant. This plant produces Extra Neutral Alcohol (ENA), which is used in the manufacture of alcoholic beverages. The plant capacity is 100 KL per day. The fermented wash (also called beer) containing about 8 (min)-14 (max)% ethanol is fed on a continuous basis to the distillation section for producing IS, RS, and ENA.
Modeling the unit
All the relevant datasheets, process descriptions, standard & emergency operating procedures, and drawings were analyzed for the data required for building the dynamic model.
Keeping the data gaps, project schedule, and the end-use of the model in mind, it was decided to target a model matching design and operating data within +/- 5% but lean enough to run in real-time. The heart of the model is the distillation train, shown below in the figure below:
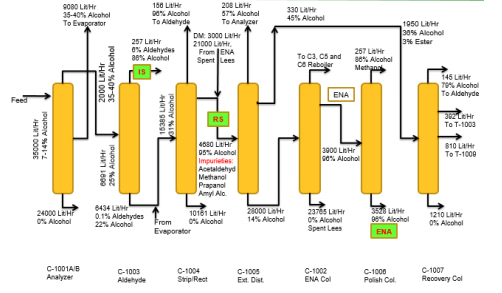
Fine-tuning the PID controllers was the key to achieving correct performance. The integrated model was configured for:
- Proper control response
- To study the impact of design changes on operations
To study the interaction between Distillation and Evaporation plants
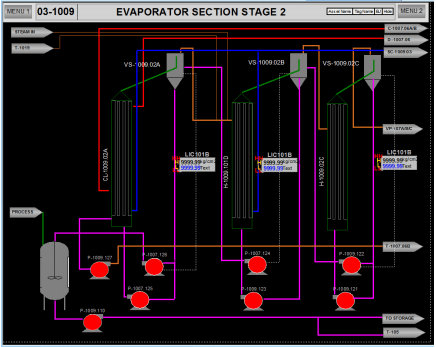
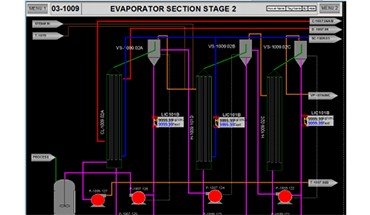
The integrated model was configured & tested to:
- Achieve proper control response
- Take startup & shutdown of the plant as per client’s procedure
- Operator response to various malfunctions e.g. pump failure, heat exchanger leak, indicator value offset, etc
- Performance of Evaporator section at various operating conditions of temperature & flow & compare various operating strategies to enhance the ethanol purity e.g. changing recycle of side-cut draw flow
Some of the important points were to match:
- Removal of Aldehyde in Aldehyde column
- Ethanol composition in ‘Spent Lees’
- Removal of Methanol in Polishing Column
A team of client engineers and operators performed an actual shutdown & startup of the plant successfully, as part of the Model Acceptance Test.
Challenge:
To address the engineering and operator training needs of an Ethanol plant.
Solution:
Develop a detailed steady-state and dynamic model of the complete plant including a distillation section having the following columns:
- Analyzer Column
- De-Gasifying Column
- ENA Column
- Aldehyde Column
- Stripper-Rectifier Column
- Extractive Distillation Column
- Polishing Column
- Recovery Column
- Evaporation section having two stages: Stage I Evaporation and Stage II Evaporation
The model was integrated with the HMI graphics. Standard startup and shutdown were carried out on the integrated model.
Learning:
- The separation efficiency is very sensitive to column opera4ng pressure & evaporator performance
- The complex heat integration presents challenges
Benefits:
- Replica of an existing plant for real-life training for plant operators
- The steady-state was used during engineering to optimize the design
- Insight into interactions between Distillation and Evaporation section